A robot is a machine that should handle motion and manipulation with objects. It should be able to obtain information about his environment and he should be able to influence it itself.
The word robot itself comes from the Czech drama by Karel Čapek: R.U.R. (1921). The word began to primarily refer to mechanical humans, animals, and other beings. Today, we use the word to describe all the machines that replaces humans in strenuous work.
The 4 different types of robots
1. Appliance
Does housework independently (eg robotic vacuum cleaner, mixer, dishwasher, etc.)
2. Manipulator
The machine has no intelligence of its own and is controlled remotely.
3. Android
The machine has its own intelligence. This category divides into:
- Droid = Any automatic robot, its type is also a drone.
- Humanoid = A robot that has similar behaviour and thinking as humans. Humanoid robots have arms and legs that mimic human movement. For example, NASA uses this type of robot to test spacesuits.
Note: Android is also a name for the operating system from Google.
4. Cyborg
Cyborg is a short for cybernetic organism. It is a combination of organic and mechanical parts. The cyborg has a biological body and brain that is under the control of the machine through a bio-cybernetic connection. Cyborgs are primarily found in sci-fi works, but actually people with mechanical implants can be already considered as cyborgs.
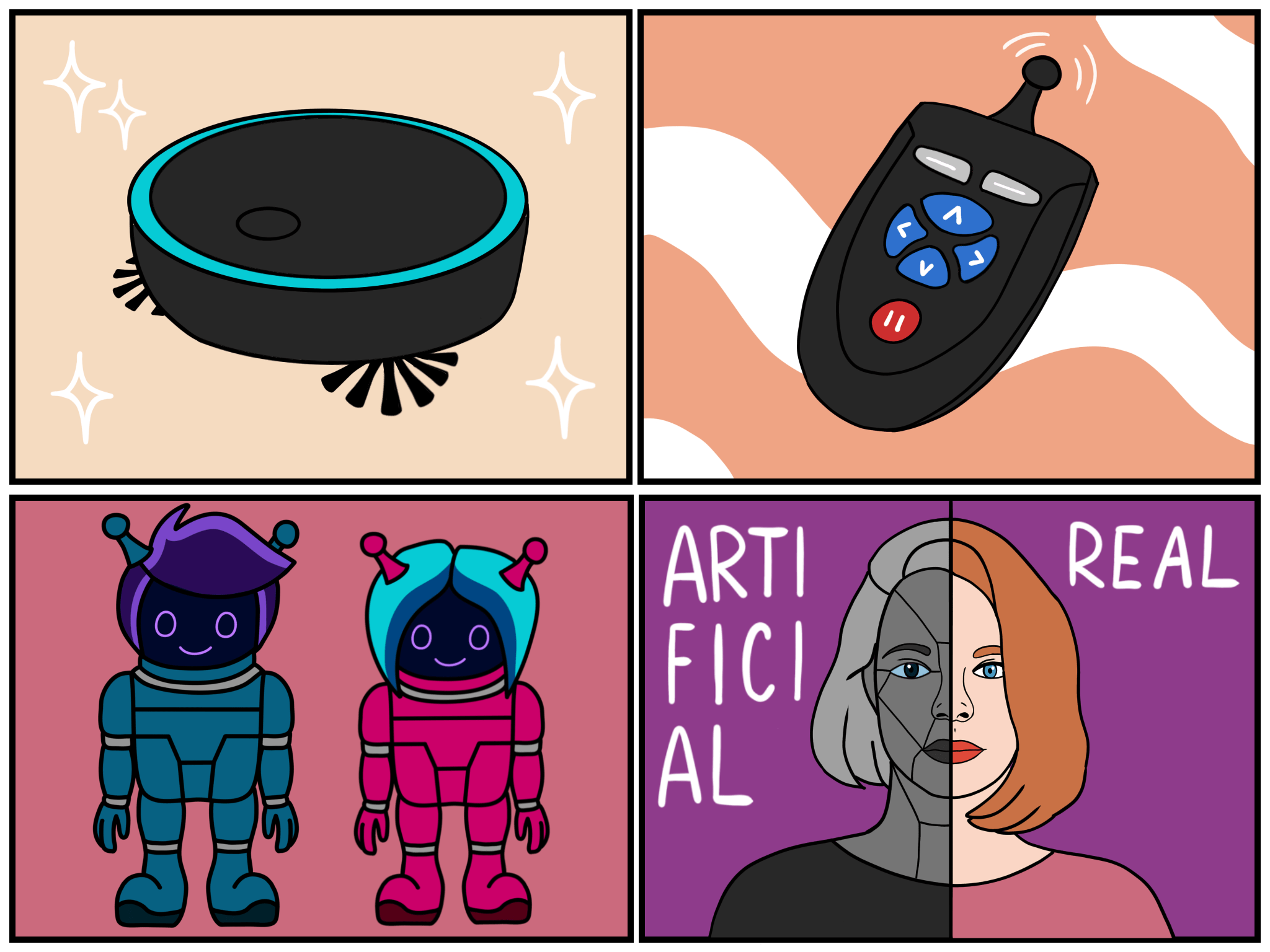
The four basic types of robots. A robot vacuum cleaner is a great example of a typical home appliance. Robots with no own intelligence are controlled by a remote controller. Humanoid robots look like humans and maybe they will be a part of the society in the future. And so would cyborgs, people with mechanical parts.
Robotics
Robotics is a science that deals with the study and design of robots and similar devices. It focuses on artificial intelligence, but also mechanical, electrical and other fields. The first area where robotics gained its usage was the automotive industry.
In the 1980s, Japan took the lead in the use of robots. Machines were equipped with tactile sensors and computer vision. In 2000, the Japanese company Honda introduced the first humanoid robot, Asimo.
Asimo was designed to live in a natural human environment. It can move independently (walk, jump, dance), recognize and respond to human speech. Other well-known robotics companies are Boston Dynamics, iRobot (USA), Sony, Seiko Epson (Japan), Hanson Robotics (China), etc.
Robotics largely affects human life in many ways. Robots can operate in hazardous environments, from industrial factories to planetary exploration. But they can also be used to repair parts of the human body in the form of prostheses.
Laws of robotics
Robotics is also connected with studying and building artificially intelligent machines to better understand living beings. Today, we have 3 basic laws of robotics defined by scientist and science fiction writer Isaac Asimov. Later he added the “Zero Law”, but it has caused a lot of controversy and it’s not considered as a fundamental law:
- A robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm.
- A robot must obey the orders given it by human beings except where such orders would conflict with the First Law.
- A robot must protect its own existence as long as such protection does not conflict with the First or Second Law.
Law Zero: A robot may not harm humanity, or, by inaction, allow humanity to come to harm.[1]
[1] Three Laws of Robotics. Wikipedia: the free encyclopedia [online]. San Francisco (CA): Wikimedia Foundation, 2001- [cited 2022-06-02]. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Three_Laws_of_Robotics